Draft amendment to Poland’s KSeF – mandatory e-invoicing from 2026, key changes and what it means for businesses
The Polish Ministry of Finance has published a new draft amendment to the VAT Act, which introduces the obligation to issue e-invoices via the National e-Invoicing System (KSeF). This system is set to become a universal and mandatory tool – first for large businesses, and later for all other VAT taxpayers operating in Poland. The draft, released on 11 April 2025, outlines a number of technical and procedural changes aimed at making the transition to the new invoicing model smoother.
It is important to underline that the proposed solutions are still part of a draft law and may be subject to further changes during the legislative process. The final version of the regulations will be known only once the public consultation has concluded and the amendment is formally adopted. This means that companies must work on two fronts: keeping track of legal developments and already preparing internally to avoid being caught unprepared.
This article summarises the main assumptions of the amendment, key implementation deadlines, the planned rollout of the KSeF system in Poland, and practical tips on how to prepare your business for the upcoming e-invoicing obligation.
In this article:
When will KSeF become mandatory?
According to the latest draft amendment to Poland’s VAT Act, the obligation to use the National e-Invoicing System (KSeF) will be introduced in stages, depending on the size of the business and the value of its sales in 2024. The Ministry of Finance has made it clear that historical data, not future projections, will determine the applicable deadline.
Stage I – large taxpayers from 1 February 2026
The first stage will cover large entities whose total sales value (including VAT) exceeded PLN 200 million in 2024. For these companies, the use of KSeF will become mandatory from 1 February 2026. Importantly, the reference year is 2024, not 2025 as initially planned, meaning that many businesses can already estimate whether they will fall into this group.
Stage II – all other taxpayers from 1 April 2026
From 1 April 2026, the obligation to use KSeF will apply to all remaining taxpayers, including both VAT-registered and VAT-exempt entities. This stage covers the majority of businesses, including small and medium-sized enterprises.
Micro-entrepreneurs – until 2027
Micro-entrepreneurs considered will benefit from an additional postponement. If their monthly turnover does not exceed PLN 10,000 and individual invoices do not exceed PLN 450, they will be required to use KSeF only from 1 January 2027.
Key changes in the draft amendment to the Polish VAT Act
The published draft amendment includes several key changes relevant for businesses preparing for the mandatory use of the National e-Invoicing System (KSeF) in Poland. Although the proposal is still under consultation, many of the suggested solutions reflect requests made by the business community. Below is an overview of the most important changes which – if adopted in their current form – will significantly impact how VAT reporting is handled.
Offline24 mode – becoming a permanent option
One of the most significant changes is the introduction of the so-called “offline24” mode as a permanent solution. It allows invoices to be issued outside of KSeF, provided they are submitted to the system by the end of the next business day. Originally intended as a temporary measure, it will now remain a regular option – particularly useful in cases of system failures, poor connectivity, or transactions involving foreign partners and consumers.
Invoice issuer certificate
With the introduction of the mandatory KSeF and the permanent possibility to issue invoices offline24, entrepreneurs will be required to use a so-called invoice issuer certificate. This will serve to authenticate the taxpayer in the KSeF system and confirm the authenticity and integrity of the issued documents.
This certificate will be a prerequisite for legally issuing invoices offline – both in emergency situations (e.g. temporary unavailability of KSeF) and when the taxpayer decides to use the offline24 mode during the mandatory KSeF period.
The certificate will be available from 1 November 2025, allowing businesses to prepare their internal systems and procedures in good time.
Attachments to e-invoices
The draft introduces the ability to attach structured annexes to e-invoices, which is particularly useful for sectors such as utilities or mass billing. Attachments must comply with the FA(3) format and cannot contain arbitrary content – protocols of acceptance or detailed work descriptions are not permitted. Sending invoices with attachments will require prior notification by the e-Tax Office (e-Urząd Skarbowy).
Increased VAT exemption threshold
Another long-awaited change is the increase in the VAT exemption threshold from PLN 200,000 to PLN 240,000, effective from 1 January 2026. While this is positive news for small businesses, some experts note that in light of inflation, a higher increase might have been more appropriate.
Unified invoice issue date
Whether an invoice is issued online directly via KSeF or generated in offline24 mode (outside the system and submitted later), the invoice issue date will be the one indicated by the taxpayer in field P_1 of the document. This means that even if the invoice is physically transmitted to KSeF with a delay – for example, the following day – the official issue date remains the one stated by the issuer.
Although seemingly minor, this change has significant practical implications. Until now, businesses faced uncertainty regarding the moment at which an invoice was formally considered issued – especially in cases of transmission delays, system errors or technical failures. The new rule ensures consistency throughout the lifecycle of electronic invoices.
Postponement of obligations and penalties
The current draft amendment to the Polish VAT Act provides for significant deferrals of obligations and sanctions related to the implementation of KSeF, which are intended to facilitate a smooth transition for businesses to the new e-invoicing model. This approach aims to reduce regulatory pressure during the first period of the system and allows companies to implement the new solutions at a safe pace.
Key postponements include:
- No obligation to include the KSeF number in payment titles – until the end of 2026. This is especially helpful for businesses handling large transaction volumes and using banking systems that do not allow full automation in this area.
- No penalties for KSeF invoicing errors – until the end of 2026, no financial penalties will be imposed for errors such as late invoice transmission, incorrect data formatting, or improper use of offline issuance. In practice, this constitutes a “grace period” in which tax authorities are expected to focus on education rather than enforcement.
- Invoicing via cash registers allowed until 31 December 2026 – businesses may continue issuing invoices using fiscal cash registers, as well as simplified invoices (receipts with a VAT ID), without having to switch immediately to structured e-invoices.
Importantly, penalties for non-compliance with KSeF requirements will take effect only from 1 January 2027. This gives businesses additional time to review their internal processes, update software, train personnel, and implement the new system without the risk of immediate financial consequences. Nevertheless, it’s important to note that once the transitional period ends, non-compliance may result in sanctions.
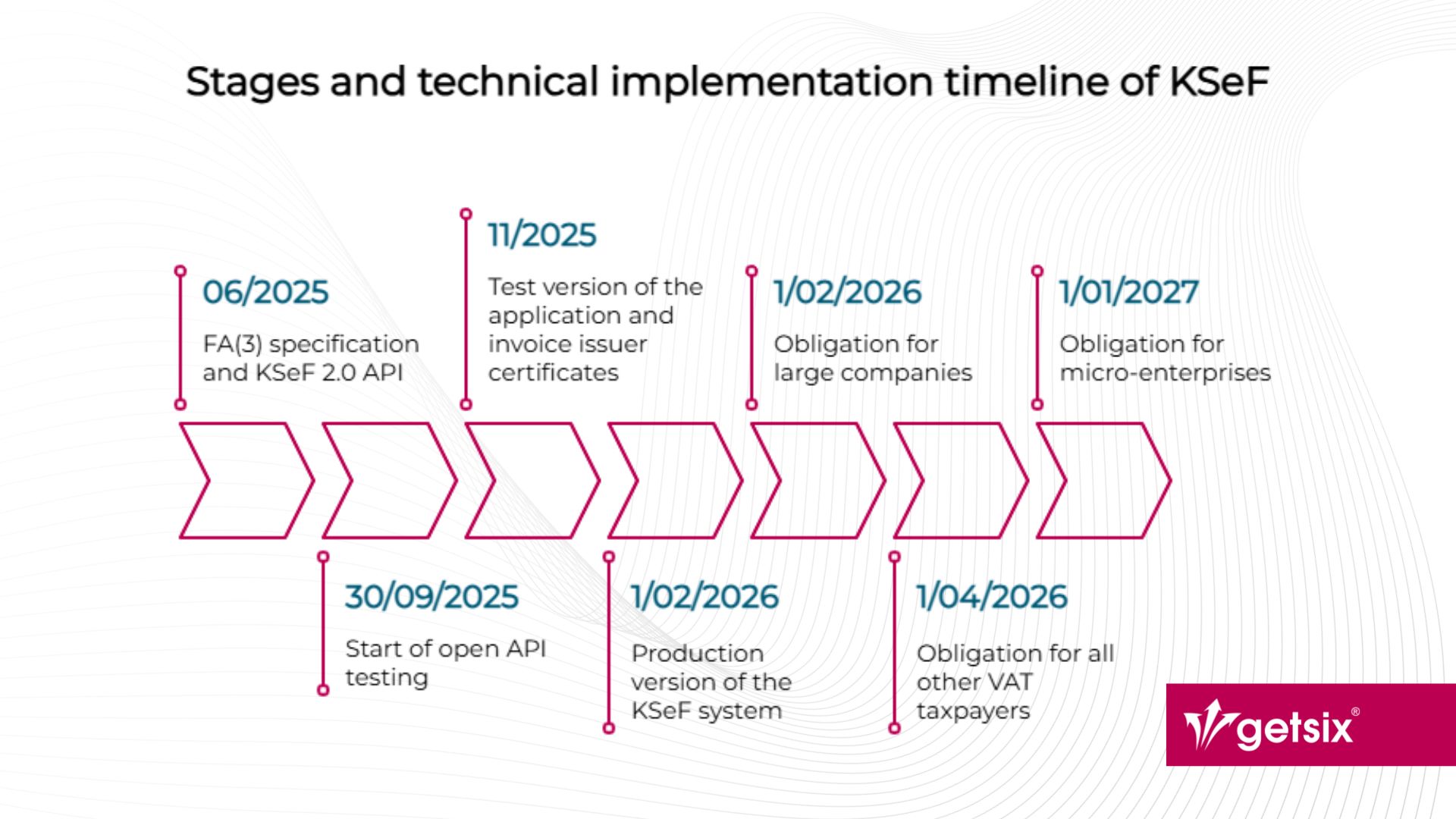
Technical implementation timeline of KSeF
The introduction of mandatory KSeF in Poland involves not only legislative changes but also the preparation of adequate technical infrastructure by businesses and software providers. The Ministry of Finance has published a detailed roadmap for system integrators, entrepreneurs and developers. Understanding this timeline is crucial – not only to meet implementation deadlines but also to test and verify the proper integration of systems with KSeF 2.0.
June 2025 – publication of technical specifications
In mid-2025, the updated version of the structured invoice format (FA(3)) and the API documentation for KSeF 2.0 will be published. These will serve as reference materials for all entities planning to integrate with the system – whether directly or through external providers.
September 2025 – open API testing
From 30 September 2025, open API testing of KSeF 2.0 will begin. It will be available to all integrators and large companies, allowing them to verify the compatibility of their financial and accounting systems with Poland’s national e-invoicing infrastructure.
November 2025 – test application and certificates
In November 2025, the following steps are planned:
- Release of the test version of the KSeF 2.0 Taxpayer Application, enabling users to explore new functionalities without generating legally binding documents.
- Launch of the process to obtain the invoice issuer certificate, which will be required for issuing invoices in offline and offline24 modes.
These tools will give businesses time to prepare their internal processes, test contingency procedures and implement technical solutions well in advance.
February – April 2026 – obligation comes into force
- 1 February 2026 – launch of the production version of the KSeF 2.0 system and the beginning of the obligation for large taxpayers.
- 1 April 2026 – extension of the obligation to all other taxpayers.
This will be a critical period for businesses planning to use internal ERP systems, accounting outsourcing or integrated invoicing applications. Proper preparation for integration will be essential to ensure operational continuity, security and compliance with new regulations.
What does KSeF mean for your business?
The introduction of the mandatory National e-Invoicing System (KSeF) in Poland is not just a change in how sales documents are issued – it represents a true transformation of financial and accounting processes within companies. While KSeF offers a range of benefits, its implementation can also present technological and organisational challenges – especially for businesses that have not yet begun any preparations.
Benefits of implementing KSeF
- Faster VAT refunds – taxpayers using KSeF may receive VAT refunds within 40 days, instead of the standard 60.
- No need to archive invoices – documents issued in KSeF are stored centrally, significantly reducing administrative burdens.
- No duplicates required – invoices cannot be lost, destroyed or misplaced – they will always be accessible in the system.
- Greater data security – KSeF ensures the integrity and authenticity of invoices through electronic signatures and unique identifiers.
- Automation and time savings – it will be possible to directly import invoice data into accounting systems, eliminating manual data entry.
- Simplified tax audits – invoices stored in KSeF will not need to be sent to authorities, e.g. as part of JPK_FA reports.
Challenges to consider
- IT systems modernisation – companies must ensure their financial software supports FA(3) structure and KSeF 2.0 API requirements.
- Employee training – staff will need to understand how to issue structured invoices in both online and offline modes.
- Changes to document workflows – many businesses will need to reorganise their sales and accounting processes.
- Exception and failure management – it will be essential to prepare for KSeF downtimes or technical disruptions.
- New procedural obligations – such as registering attachments, applying for certificates, and monitoring correct invoice submissions.
For many businesses, KSeF could be a driving force for automation, systems integration and improved operational efficiency. However, without adequate preparation, it could also become a source of stress, compliance risks and operational disruption.
How to prepare for KSeF
Although the obligation to use KSeF will not come into force until 2026, the time for preparation is shorter than it seems – especially considering the scale of the changes, which affect both technological and organisational aspects of doing business. Below are five key steps that will help your company navigate the transition smoothly and avoid unnecessary complications.
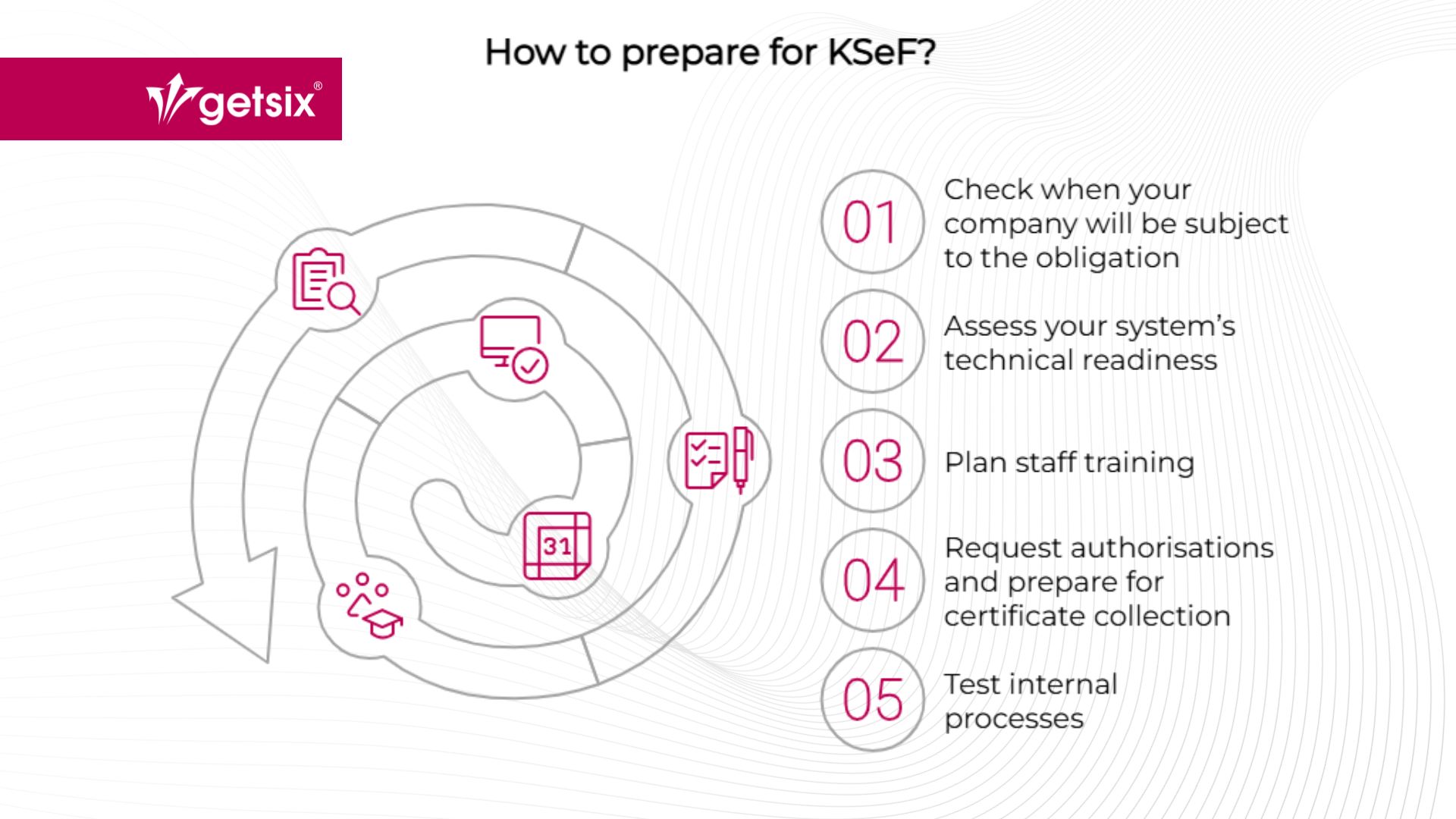
1. Check when your company will be subject to the obligation
Verify your sales value for 2024 (including VAT). If it exceeds PLN 200 million, the obligation to use KSeF will apply from 1 February 2026. Otherwise, the starting date will likely be 1 April 2026. Micro-entrepreneurs who meet specific criteria may benefit from an extension until 1 January 2027.
2. Assess your system’s technical readiness
Check whether your current accounting software:
- supports the FA(2) invoice structure and is ready for FA(3),
- can communicate with the KSeF 2.0 API,
- allows invoice issuance in offline24 mode,
- supports structured attachments (if required in your industry).
It’s worth consulting your software provider or IT integrator – especially if you are using customised systems.
3. Plan staff training
New obligations mean new procedures for issuing invoices. Plan training sessions for:
- your accounting and finance team,
- sales staff responsible for issuing invoices,
- employees handling system integration and IT infrastructure.
4. Request the necessary authorisations and prepare for certificate collection
From 1 November 2025, it will be possible to obtain invoice issuer certificates, which are essential for issuing invoices in offline and offline24 modes. It’s important to decide in advance who in your company will be responsible for handling these credentials and maintaining access.
5. Test your internal processes
Before KSeF becomes mandatory, make sure to test:
- issuing sample invoices (e.g. using the Ministry of Finance demo environment),
- the process of sending e-invoices to buyers,
- document workflows in case of system failures,
- compliance of invoices with FA(3) structural requirements.
The introduction of mandatory KSeF is one of the most significant changes to Poland’s tax system in recent years – both technologically and operationally. The aim is to increase transparency in business transactions, reduce VAT fraud, and simplify many administrative duties for businesses. At the same time, the transition requires comprehensive preparation – from updating software and internal procedures to staff training.
Although the draft amendment is still under consultation and may be revised, the current assumptions are detailed enough to serve as a solid basis for planning. And with 2026 approaching fast, the time to act is now.
If you have any questions regarding this topic or if you are in need for any additional information – please do not hesitate to contact us:
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIPS DEPARTMENT

ELŻBIETA
NARON-GROCHALSKA
Head of Customer Relationships
Department / Senior Manager
getsix® Group
***














