Workflow automation and more specifically a Business Process Management System (BPMS) is the solution that will help alleviate and solve many of the business and technical problems described thus far.
Business Process Management (a catch all description for anything process automation related) is a business management discipline combined with technology, which enables an organisation to analyse, model, automate and redesign their business processes in a way that improves business effectiveness.
The Business Problem
In most organisations, business processes are pervasive, but are predominantly manual and where automated, they tend to be isolated to a single area or department. This organisational complexity and use of selective silo based IT enablers (function specific silo applications), means that management and operational challenges manifest themselves in various ways:
- Management and employees have difficulty in making correct decisions due to not having accurate and timely information;
- Information is of devoid of business context (not seen in as part of a business process) and therefore may lead inconsistent decisions;
- Planning is often difficult due to ‘broken’ workflows, poor working practices and inconsistent information.
IT systems that support the various business processes act as inhibitors rather than enablers, as they are typically designed deployed and managed as information islands or stove pipes. This is further exacerbated by the lack of systems integration leading to no easy way of getting a single view of the truth.
Enforcing business rules, policies and procedures is an arduous task due to poor process visibility, accurate real time information and no integrated or consistent auditing. Employees are forced to work in ways, using tools that are not always very productive, efficient and can in many cases lead to rework and hidden costs. This can include the need for a user to login to various applications, using various different user interfaces to complete a simple task.
What is Business Process Management?
Business Process Management (BPM) means a comprehensive management tool which has integrated the various aspects of a business; starting from process management, as an entry point to improve business management. The BPM is an IT tool used for methodical operation and solutions, while promoting human – human, human – system, and system – system integration and regulation according to changes in the business environment. Emphasizing cross-application, cross-department, and cross-partner and client operation, the BPM through the internet achieves continuous upgrading and business optimisation through tasks such as: information transfers, data synchronisation and business monitoring. Not only does BPM cover the process deliverance and monitoring of traditional ‘workflows’, but it also overcomes the technical bottlenecks that have hindered the traditional workflows. BPM makes it possible for enterprises to reduce cost and maximise profit through the modelling, automation, management, monitoring and optimisation of the whole life cycle of internal and external business processes. BPM brings about a new era for the business management concept and makes it possible for businesses to reduce cost, maximise profit through modelling, automation, management and monitoring, and optimisation of the whole life cycle of internal and external business processes.
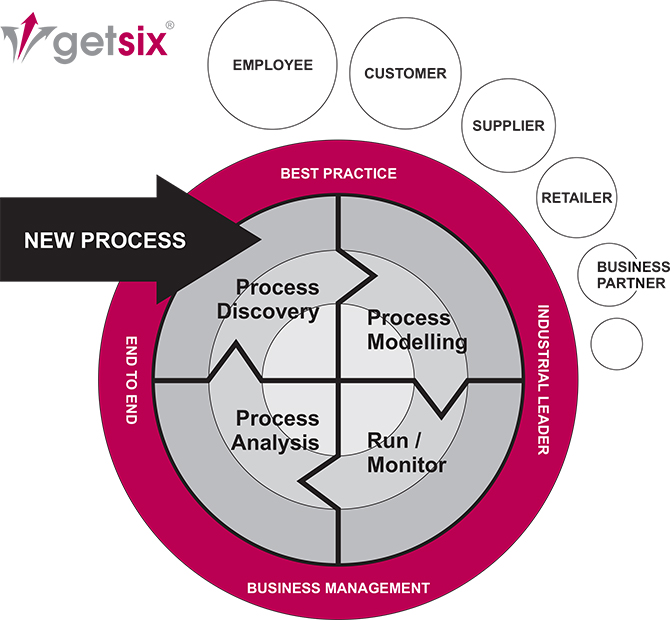
Through years of BPM project implementation we have learned, ‘each client faces unique challenges and opportunities. The core to obtain strength is to have a unique process. With this unique process, your company will survive and thrive in the fierce industrial competitions.’
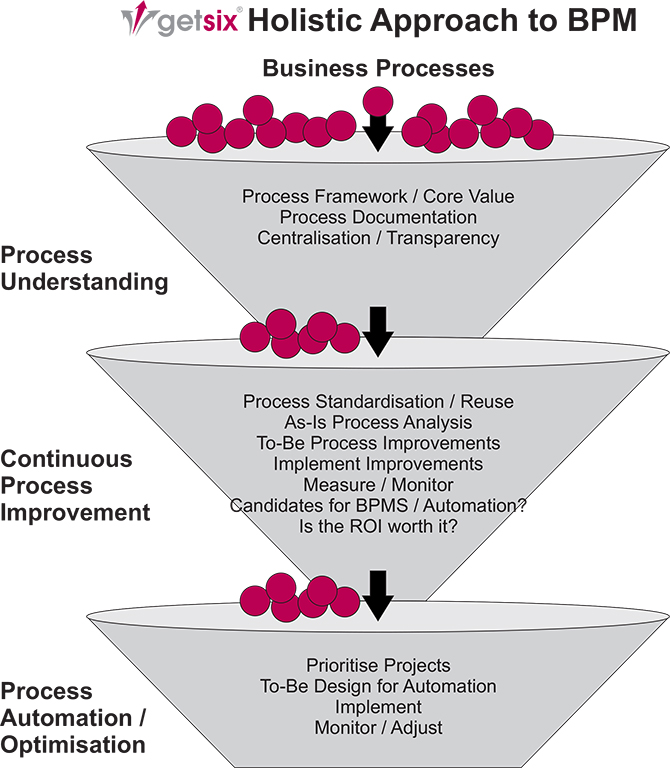
Overview
A key goal of BPM is to align processes with business goals, seek ways to improve those processes and then establish measurements that can be used to track and monitor performance for continuous improvement and optimisation. Ideally, BPM is embraced as an enterprise wide strategy. (Although it is possible to certainly apply the BPM method or BPM Software to a single process). As the diagram shows, an enterprise-wide BPM initiative fundamentally has three ‘tiers’.
Tier 1 – Process Understanding
Using a process framework, you can begin to document your processes with a focus on those processes that are core to the value you deliver to your customers. Establishing a standard approach to document your processes and creating a central repository, is a key ingredient here.
Tier 2 – Process Improvement
In terms of improvement, here is where a formal methodology (like Lean Six Sigma or some hybrid method) may be applied. Organisations will typically organise workshops to dissect their business processes, identifying process inefficiencies, then recommending and implementing process improvements.
Tier 3 – Process Automation/Optimisation
Once you have established a method for improvement and applied improvements, a subset of processes can potentially benefit from various types of technology. Workflow can enforce the way processes are performed. Process monitoring can track and audit work and provide insights to process bottlenecks and problems. Automation can eliminate activities performed by people, as well as eliminate human mistakes. SOA and BPM technology can be used to augment/enhance current business systems or develop entirely new business systems to support re-engineered processes.
There are five stages in a BPM life cycle:

Design, Modelling, Execution, Monitoring and Optimisation.
Design
Process design encompasses both the identification of existing processes and the design of ‘to-be’ processes. The areas of focus include representation of the process flow, the actors within it, alerts & notifications, escalations, standard operating procedures, service level agreements and task hand-over mechanisms.
Modelling
Modelling takes the theoretical design and introduces combinations of variables (e.g. changes in rent or materials costs, which determine how the process might operate under different circumstances).
Execution
One of the ways to automate processes is to develop or purchase an application that executes the required steps of the process; however, in practice, these applications rarely execute all the steps of the process accurately or completely. Another approach is to use a combination of software and human intervention; however this approach is more complex, making the documentation process difficult.
Monitoring
Monitoring encompasses the tracking of individual processes, so that information on their state can be easily seen, and statistics on the performance of one or more processes can be provided. An example of the tracking is being able to determine the state of a customer order (e.g. ordered arrived, awaiting delivery, invoice paid), so that problems in its operation can be identified and corrected.
Optimisation
Process optimisation includes retrieving process performance information from modelling or monitoring phase; identifying the potential or actual bottlenecks and the potential opportunities for cost savings or other improvements; and then, applying those enhancements in the design of the process. Overall, this creates greater business value.
What makes BPM and Workflow different?
If you follow the information technology industry and Enterprise Content Management (ECM) world then you have heard the terms Business Process Management (BPM) and Workflow. They both share similarities, but they have unique functionalities. The grey area for some people has to do with how the terms BPM and Workflow are often referred to as BPM Workflow Automation. They both address the need to automate core business processes to eliminate bottlenecks, cut our redundancies, and achieve efficiency, in their own specialised ways. BPM characterises a series of activities that are independent from specific applications and systems. Workflow facilitates simple routing of tasks or activities from person to person.
Workflow Automation Software:
Workflow Automation Software uses application specific sequencing of tasks set up with predefines rules, including either automated or manual activities. A Workflow is usually set up on a fixed business process and you will have to tell the system how to deal with exceptions to the predefined rules. Microsoft Sharepoint is an example of an ECM system that uses workflows and that uses an intuitive learn by example approach. This makes the system smarter over time as it learns every time you process an exception, new vendor, or data type, so the next time that type of information is capture the system will automatically be able to process the information accurately and accordingly. Workflow automation solutions run on smart process apps that basically take your manual business processes and replicates them electronically in a more efficient, smarter way.
Please learn more:
Business Process Management Software:
Now when you talk about BPM, it is distinguished by its ability to co-ordinate activities among users. It connects different systems by enabling a seamless data share and universal control function of the business critical data from one central interface. Whether that interface is Sharepoint, another type of Document Management system or ERP system like MS Dynamics NAV, BPM makes it so that you have quick access and control to the data you need right from inside the applications you live in the most. Business processes, once they are defined, can be modelled, automated, and managed to help you realise maximum efficiency to lower your costs and achieve higher operational output. By following set rules, BPM is able to distinguish between exception rules and the actual flow of your business processes that allows you to govern every process. Information and data is constantly coming into your organisation from outside sources and through BPM tools like Kofax TotalAgility (KTA) and Kofax Transformation Modules (KTM) you are able to capture, evaluate and analyse the information efficiently and effectively.
Please learn more:
These topics go deeper and into more detail. If you have any questions, or would like some more specific information, then please contact us, so we can help answer your questions!
To provide our Business Process Automation Solutions. We are using the above mentioned Enterprise Class Software that our customers will receive the most value out of BPM like.
The BPM technology is a part of our Business Model and Vision and together with our Cloud Solutions, we are able to offer our state-of-the-art solutions with the scope of services in the area:
- Full Service Solutions;
- Business Process Outsourcing;
- Industry Specific (Vertical Process) Solutions.
The BPM layer
The process layer, positioned between business users and back-end systems (See illustration below). One of the back-end systems at the bottom is the core application that was the subject of the assessment (for example, ERP like MS Dynamics NAV or Billing). The BPM solution makes use of these core business applications and legacy systems, and provides an extra value-add layer between these systems and the business users.
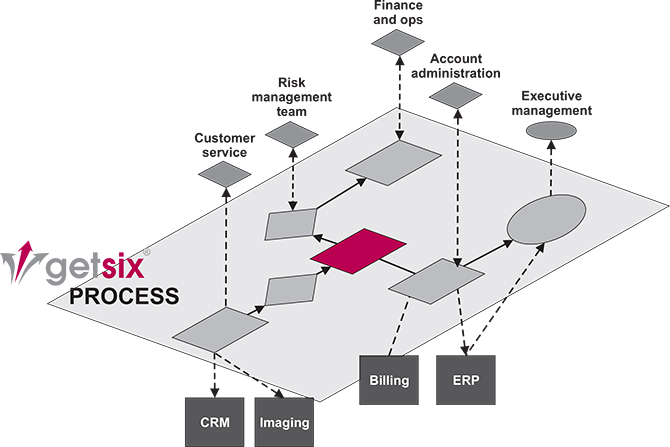
Adding the process (BPM) layer alleviates a significant number of the challenges:
- Automating business policies, workflows and decision making;
- Reducing error and improving consistency;
- Standardising procedures across geographies or markets;
- Providing visibility and control to team leads, managers and workers;
- Alerting for critical events and initiating actions.















